HTML Introduction
18 March 2025 | Category: HTML
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is the foundation of every webpage. It defines the structure and content of a website using elements and tags. Browsers read HTML documents and render them as visual web pages.
In this guide, we’ll cover:
✅ What is HTML?
✅ A Simple HTML Document
✅ HTML Boilerplate
✅ What is an HTML Element?
✅ How Browsers Read HTML?
1. What is HTML?
Definition:
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is a markup language used to create webpages. It structures text, images, videos, and links on a webpage using tags.
Key Features of HTML:
✔ Defines the structure of web pages
✔ Works alongside CSS (for styling) and JavaScript (for interactivity)
✔ Uses tags (like <p>, <h1>, <a>) to format content
✔ Supports links, forms, images, videos, and tables
✔ Browser-friendly
Example of HTML Code:

2. A Simple HTML Document
An HTML document is a text file containing HTML code that browsers interpret to display content.
Example of a Basic HTML Document:

Explanation:
✔ <!DOCTYPE html> – Defines the document type as HTML5
✔ <html> – Root element of the document
✔ <head> – Contains metadata (title, links, styles)
✔ <title> – Defines the page title (important for SEO)
✔ <body> – Contains visible content (text, images, links)
3. HTML Boilerplate (Standard Structure of an HTML Page)
A boilerplate is a basic template that includes the essential HTML elements required for every webpage.
HTML Boilerplate Code (Best Practice)

Key Components of the HTML Boilerplate:
✔ <!DOCTYPE html> – Specifies the document type (HTML5)
✔ <html lang="en"> – Defines the document language (important for SEO)
✔ <meta charset="UTF-8"> – Ensures proper character encoding
✔ <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> – Makes the page mobile-friendly
✔ <meta name="description"> – Helps search engines understand page content
✔ <meta name="keywords"> – Specifies keywords (not a major SEO factor anymore)
✔ <meta name="author"> – Specifies the page author
✔ SEO Benefit: A proper boilerplate improves indexing, enhances user experience, and boosts ranking.
4. What is an HTML Element?
An HTML element is a complete unit that consists of an opening tag, content, and closing tag.
Example of an HTML Element:

✔ <p> – Opening tag
✔ This is a paragraph. – Content
✔ </p> – Closing tag
Types of HTML Elements:
🔹 Block-level elements (e.g., <div>, <p>, <h1>–<h6>, <section>, <article>)
🔹 Inline elements (e.g., <span>, <a>, <b>, <i>)
✔ SEO Benefit: Using semantic elements (<header>, <article>, <nav>) improves SEO and accessibility.
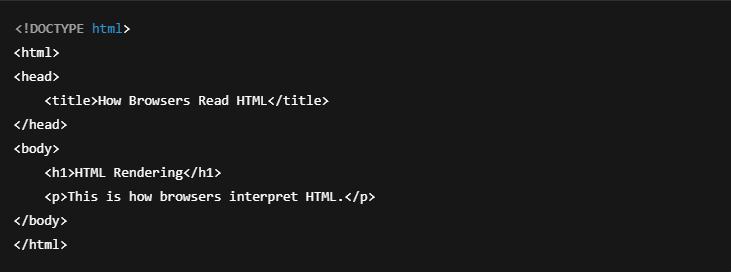
5. How Browsers Read HTML (Rendering Process)
Browsers render HTML in five main steps:
1️⃣ HTML Parsing: Browser reads the HTML file line-by-line
2️⃣ DOM Tree Creation: Builds a Document Object Model (DOM)
3️⃣ CSS Parsing: Reads and applies CSS styles
4️⃣ JavaScript Execution: Executes JavaScript code for interactivity
5️⃣ Rendering & Painting: Combines HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to display content
Example of HTML Rendering Process: